 PDF(5502 KB)
PDF(5502 KB)


 PDF(5502 KB)
PDF(5502 KB)
 PDF(5502 KB)
PDF(5502 KB)
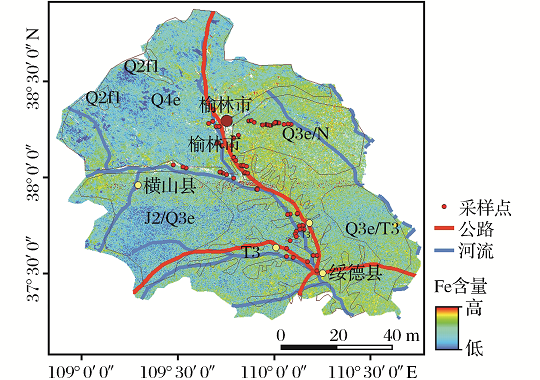
黄土高原土壤铁元素含量遥感反演方法
 ,
{{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
,
{{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
Remote Sensing Inversion Method of Soil Iron Content in the Loess Plateau
 ,
{{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
,
{{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |