

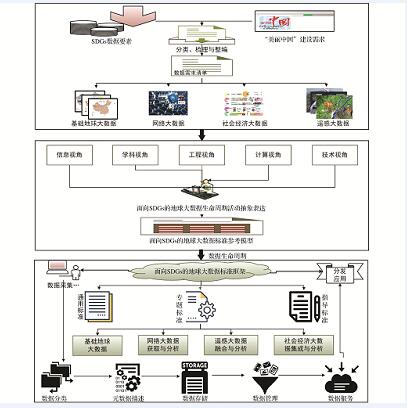
面向SDGs和美丽中国评价的地球大数据集成框架与关键技术
王卷乐, 程凯, 边玲玲, 韩雪华, 王明明
遥感技术与应用 ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5) : 775-783.
面向SDGs和美丽中国评价的地球大数据集成框架与关键技术
 ,
{{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
,
{{javascript:window.custom_author_cn_index++;}}
Integration Framework and Key Technology of Big Earth Datafor SDGs and Beautiful China Evaluation
 ,
{{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
,
{{javascript:window.custom_author_en_index++;}}
| {{custom_ref.label}} |
{{custom_citation.content}}
{{custom_citation.annotation}}
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |